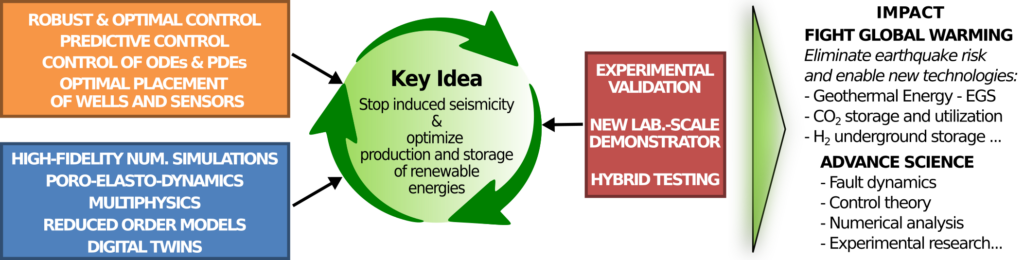
Climate change poses an imminent threat to our civilization. Prominent new technologies to fight climate change involve the earth’s underground renewable and sustainable energy resources and underground storage. However, all these technologies depend on the injection of fluids into the earth’s crust, which, in turn, can cause significant earthquakes. INJECT will solve this problem on the basis of a new, ground-breaking scientific method that will prevent human-induced seismicity and will maximize energy production and storage from renewable and sustainable natural resources.
INJECT’s interdisciplinary methodology is based on an astute scientific programme that brings control theory and mathematics to the heart of this new challenging problem. Based on cutting-edge theoretical developments, robust controllers and observers will be designed to optimally adjust fluid injection rates, prevent induced seismic events over large regions and optimize energy production and storage. INJECT’s innovative theoretical methods will be thoroughly tested through high-fidelity numerical models that will account for poro-elasto-dynamics, Coulomb friction, multiphysics and reduced-order modeling. The experimental plan will build on demonstrators and hybrid lab-computer testing for testing the theory.
Environment
INJECT’s research is conducted in ENSTA Institut Polytechnique de Paris (ENSTA IP Paris) within the IMSIA laboratory. INJECT’s research group is based at the Mechanical Hub building, a collaborative space housing leading research laboratories specializing in solid mechanics, fluid mechanics, and living mechanics from ENSTA IP Paris and École Polytechnique.

Funding
INJECT is funded by the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation program (Grant agreement no. 101087771 INJECT).

